Category: Machine Learning
-
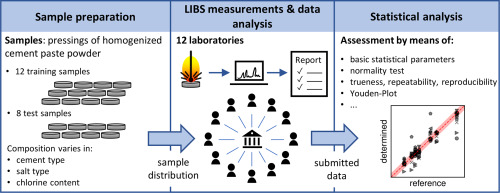
Interlaboratory Comparison for Quantitative Chlorine Analysis in Cement pastes with laser induced breakdown spectroscopy
We consider quantitative analyses of spectral data using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. We address the small size of training data available, and the validation of the predictions during inference on unknown data.
-
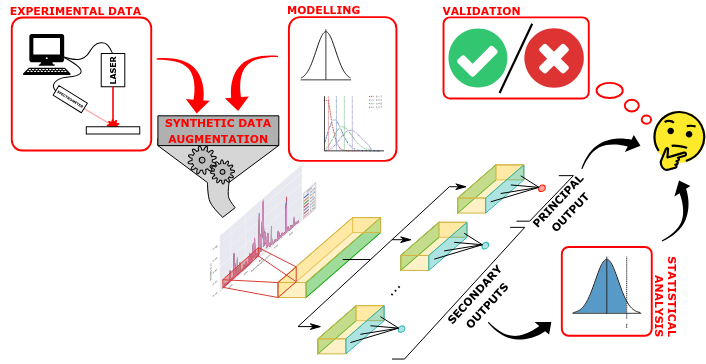
Trustworthiness of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Predictions via Simulation-based Synthetic Data Augmentation and Multitask Learning
We consider quantitative analyses of spectral data using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. We address the small size of training data available, and the validation of the predictions during inference on unknown data.
-
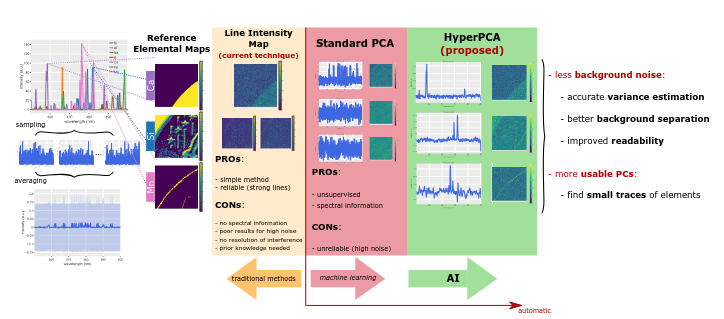
HyperPCA: a Powerful Tool to Extract Elemental Maps from Noisy Data Obtained in LIBS Mapping of Materials
We introduce HyperPCA, a new analysis tool for hyperspectral images based on a sparse representation of the data using Discrete Wavelet Transform and kernel-based sparse PCA to reduce the impact of noise on the data and to consistently reconstruct the spectroscopic signal, with a particular emphasis on LIBS data.
-
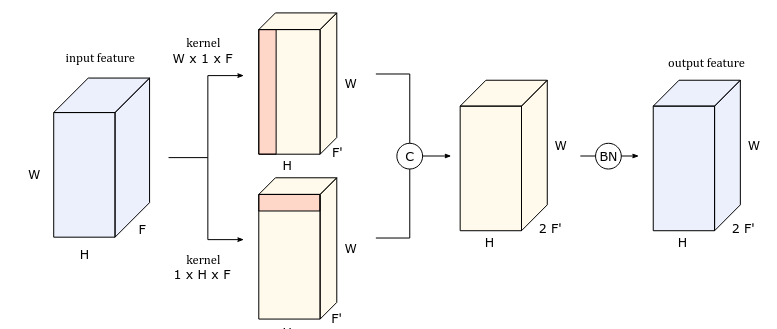
Inception Neural Network for Complete Intersection Calabi–Yau 3-folds
We introduce a neural network inspired by Google’s Inception model to compute the Hodge number $h^{1,1}$ of Complete Intersection Calabi-Yau 3-folds.
-

Deep Multi-task Mining Calabi-Yau Four-folds
We continue earlier efforts in computing the dimensions of tangent space cohomologies of Calabi-Yau manifolds using deep learning.
-
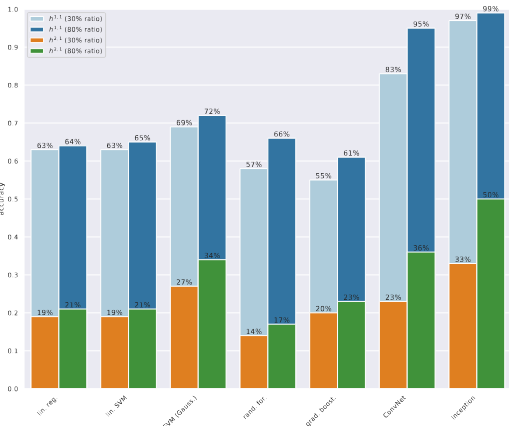
Machine Learning for Complete Intersection Calabi-Yau Manifolds: a Methodological Study
We revisit the question of predicting both Hodge numbers $h^{1,1}$ and $h^{2,1}$ of Complete Intersection Calabi-Yau 3-folds using machine learning.
